Acerca de
HoLEP Notes
Created 04Jan2022, Last edited 10Oct2023
General
HoLEP (Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate) is a minimally invasive surgical treatment for men with any degree of prostate enlargement who have urinary symptoms and men who are suffering from retention of urine, repeated urine infections or bleeding due to an enlarged prostate.
https://www.cambridgeurologypartnership.co.uk/urology-info-for-patients/prostate/holep-urolift/
HoLEP is a multi stage procedure.
1) The urethra must be able to accept calibration up to 30 F easily using Van Buren sounds to broaden the urethra. A 26–28 F continuous flow resectoscope (thin metal tube containing a light, camera, etc) is inserted into the urethra.
Saline irrigant is then run into the resectoscope.
2) A camera and Holmium:YAG (Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser with penetration of energy approximately 0.2 mm into prostatic tissue with simultaneous coagulation of blood vessels is used to separate (peel off) the prostatic tissue from the containing prostatic capsule/casing in lobes. Each lobe is pushed through into the bladder. The camera image appears large on a screen although the hand to instrument movement is 1 to 1.
3) Once all lobes have been dissected free and pushed into the bladder, the laser settings should be changed to achieve optimal coagulation. The capsular surface is then inspected carefully. Any capsular bleeders should be coagulated by first defocusing the laser and then activating it until hemostasis is achieved.
4) The final stage involves using a morcellator to chop up the lobes and suck them out of the bladder. The expelled tissue can then go for pathology analysis. HoLEP can be used on any size prostate.
This describes it in detail...
https://www.endourology.org/education-articles/holmium-laser-enucleation-of-the-prostate
Note the Pirhana Morcellator :-)
Discusses stages in detail
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC165416/
Actual camera footage by Dr Oh (54 ml size prostate)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z2T8_vVjkdc
HoLEP Information for Patients. (Cambridge Urology Partnership)
*** "HoLEP has replaced standard TURP completely and unreservedly in our hospital. There is nothing out there that has been shown to be better"
"HoLEP represents a paradigm shift in the surgical management of BPH and is endorsed by all the leading urological organizations world-wide. We have used this technique exclusively with over 2,000 patients since it evolved in the late 1990's. Once learned, HoLEP replaces both TURP and open prostatectomy, providing superior outcomes in prostates of all sizes!"
"Self-catheterisation or permanent catheter to empty bladder if the bladder is weak (1%)"
Some patients, particularly those with small prostate glands, are unable to pass urine at all after the operation due to temporary swelling of the prostate area.
"it is usual not to have any pain" = it is unusual to have any pain
The laser is used to separate the obstructing prostate tissue from its surrounding capsule
Removal of your prostate
if the prostate is fully enucleated
Finding unsuspected cancer in the removed tissue which may need further treatment (5%)
https://www.cambridgeurologypartnership.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/HOLEP-info-sheet.pdf
https://bphsurgeon.co.uk/holep/
HoLEP was developed by 2 New Zealand Urologists, Peter Gilling and Mark Fraundorfer, in the 1990′s. Since then it has been extensively researched and a large number of published clinical trials support it as the new “Gold Standard” for treating BPH.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5380818/
24 Mar 2017
Comparison of Surgical Outcomes Between Holmium Laser Enucleation and Transurethral Resection of the Prostate in Patients With Detrusor Underactivity (DU)
In the present study, we showed that HoLEP was superior to TURP with regard to postoperative Qmax, PVR, symptomatic improvement and QoL.
With the resolution of outflow obstruction, voiding is possible with low bladder detrusor muscle contractility, resulting in postoperative benefits in urinary symptoms and reduced PVR.
Both the TURP and HoLEP groups showed improvements in voiding symptoms and in other postoperative data, including QoL, IPSS, Qmax, and PVR.
Both TURP and HoLEP can be effective in patients with BPH and DU. However, our data demonstrated that patients in the HoLEP group showed significantly greater improvements than patients in the TURP group in the other parameters
HoLEP..including a lower rate of complications, less blood loss, reduced catheterization time, and shorter hospitalization.
One of the major and most common complications of TURP is the risk of bleeding.
Decreased postoperative bleeding has been one of the main advantages of HoLEP. ***
...which was ascribable to the improved efficiency of obstruction removal using HoLEP
HoLEP showed better efficacy than TURP in improving voiding symptoms, Qmax, PVR, medication requirements and in minimizing postoperative complications.
https://afju.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s12301-021-00230-1
10 September 2021 Study of studies.
Mainly of interest with Detrusor Underactivity (DUA) due to impaired contractility.
A previous study was conducted in determining the effect of HoLEP in patients with non-neurogenic impaired bladder contractility, and the results recommend HoLEP to be performed in those patients.
There is no evidence that there is a benefit for TURP in patients with DUA.
Patients with HoLEP surgery had better outcomes in the follow-up in the form of IPSS, Qmax, PVR, and catheter-free rate.
HoLEP showed better improvement in IPSS scores in patients with DUA. HoLEP can be considered to be performed in the BPH patients with DUA for better outcomes for the patients.
https://www.ics.org/2020/abstract/412
In one of these studies, 95% of patients were voiding spontaneously following HoLEP without the need to do Clean Intermittent self-Catheterization (CIC) while investigators in the other study found that 73% of patients achieved catheter-free status following HoLEP and the remaining patients needed to do CIC for high post-void residuals. Furthermore, all other studies reported an improvement in all outcome parameters and proved the efficacy of HoLEP in patients with DU and Bladder Outflow Obstruction (BOO).
*** Our review suggests that more than 80% of men with DU and BOO are likely to void spontaneously after HoLEP. This may be explained by the comprehensiveness of prostate tissue enucleation attainable with HoLEP, permitting voiding through a wide-open channel in the prostatic urethra.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33763730/
HoLEP for acute and non-neurogenic chronic urinary retention (NNCUR) how effective is it? Tevita Aho et al. World J Urol. 2021 Jul.
*** 98.8% with NNCUR were catheter-free 3 months after HoLEP.
https://www.ouh.nhs.uk/urology/services/documents/holep.pdf
"It is unusual to require a blood transfusion after laser surgery"
Internal sphincter muscle of urethra...is the primary muscle for prohibiting the release of urine.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Urethral_sphincters
females are more at risk of problems with their urinary continence, as they have a short urethra and only one bladder neck sphincter (that they go on to call the External Sphincter even though it's situated at the pelvic floor)
https://www.futurelearn.com/info/courses/understanding-continence-promotion/0/steps/46068
(With Anteroposterior dissection by Tokyo group) the transient stress urinary incontinence rate was significantly improved by 2.7% compared to 25.2% with the conventional (Classic 3-lobe technique) method.
(With En bloc technique with anteroposterior dissection by Chiba, Japan) It is also important to note that the authors made significant efforts to develop the technique to preserve the sphincter.
(At Seoul) based on the three-lobe technique - it was modified to better preserve the sphincter
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6722407/
At this step, some white and shiny circular fibers could be seen at 0.5 cm from the bladder neck, which were visually different from hyperplastic gland. This is exactly the bladder neck and internal sphincter that need to be preserved
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7844485/
Amount Remaining
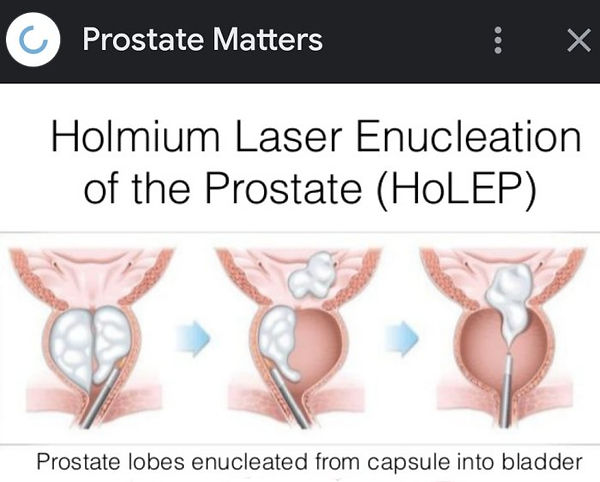
Above: Giving impression with HoLEP all lobes are enucleated from prostate.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/17917-holmium-laser-enucleation-of-the-prostate-holep
What percentage of the prostate is removed in HoLEP?
"How much of your prostate your surgeon removes depends on how large the blockage is or how much your prostate is pressing on your urethra. Typically, your surgeon removes about 50% to 60% of the total prostate volume"
"followed by enucleation of the median lobe and subsequent enucleation of both lateral lobes"
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6722407/
Prostate has five lobes.
-
Middle/Median lobe (At bottom between the two ejaculatory ducts and the urethra)
-
Right lobe
-
Left lobe
-
Lateral lobe (involves side)
-
Posterior lobe (that starts from the floor of the urethra)
-
Anterior lobe. (lying in front of the urethra, all fibromuscular tissue)
The lateral lobes (right and left lobes) form the main mass of the gland and are continuous posteriorly. They are separated by the prostatic urethra.
https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1923122-overview#a1
https://training.seer.cancer.gov/prostate/anatomy/lobes.html
HoLEP versus TURP
https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/1756287213498923
Aug 2013
HoLEP was the only procedure with...
a) a statistically significant greater international prostate symptom score (IPSS) reduction (p = 0.005) compared with TURP.
b) a statistically greater increase in maximal flow rate (Qmax) compared with TURP
There were no statistically significant differences in improvement in quality of life scores (QoL) and postvoid residual volume (PVR) between the procedures.
HoLEP was the only procedure that did not require reintervention for recurrent benign prostatic enlargement.
Mucosal bladder injury occurred in 0–18% of HoLEP patients and capsular perforation in 0–2%.
Despite more tissue being removed in HoLEP, it caused less bleeding and, therefore, there was less need for postoperative bladder irrigation, shorter catheter time and shorter length of stay for HoLEP.
HoLEP should be proposed as a potential new gold standard surgical therapy instead of TURP for patients with BPH
79% of patients having HoLEP were discharged on the day of surgery.
HoLEP was more durable
HoLEP for acute and chronic retention is as safe as HoLEP for LUTS and allows 98% to remain catheter free at a mean follow up of 5 years
TURP for men in urinary retention is associated with significant morbidity.
HoLEP for retention has low morbidity
https://www.uhhospitals.org/for-clinicians/articles-and-news/articles/2017/01/holep-provides-treatment-for-enlarged-prostate-with-fewer-side-effects
The chance for erectile dysfunction is zero with HoLEP.
https://theurologypartnership.co.uk/treatments/holep/
Has good comparison table See Advantages of HoLEP (Holmium Laser) vs. TURP
Recovery 2-4 wks (4-6 wks TURP)
*** Biopsy to Detect Hidden Prostate Cancer routine (with HoLEP)
% of Prostate Removed Economical(?) Expensive(?)

It does remove more prostate tissue than a TURP would (advantage against regrowth) but with less chance of bleeding and a shorter recovery time.
HoLEP (Holmium Laser Enucleation of Prostate) is the most advanced laser technique currently available and has been recommended by NICE
..it has been rigorously evaluated in randomised trials. It is a size independent procedure suitable for any prostate in experienced hands and highly effective at treating urinary retention.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5380818/
Postoperative voiding parameters, including peak flow rate and postvoid residual urine volume were significantly better in the HoLEP group than in the TURP group.
http://somerseturology.co.uk/news/dont-suffer-in-silence/
Taunton
This procedure (TURP) has been further refined recently through new laser techniques (such as Holmium laser enucleation of the prostate, HoLEP) to limit bleeding and reduce hospital stay.
https://www.nhsinform.scot/tests-and-treatments/surgical-procedures/transurethral-resection-of-the-prostate-turp
There are a number of alternatives to TURP that can be just as effective with a lower risk of complications. They include: HoLEP and TUVP
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29858700/
HoLEP provides a higher prostate cancer detection rate compared to bipolar TURP
Videos
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PBKYACnUmlU
HoLEP video clip with orange example
Hole Up! Amy E. Krambeck, MD Very good talk-through
24 or 28 French scope
1st cut bladder neck to verumontanum (ejaculatory ducts) that is preserved
Deepen cut to level of capsule that we leave behind
adenoma which we take
extend it into the lateral lobes, so this is incorporating in the median lobe
take cut around the apex
Right apical turn
So now I've done the right lobe
about the only time i do blunt dissection is right at the apex
teach themselves. It takes around 50 case to feel comfortable.
18:49/29:39 ...but benefits of HoLEP is it also works in people who have very weak bladders so if you have a poorly contractile bladder, um one with poor muscle function, a lot of times patients will urinate, even if they are urinating by valsava, if you can maximally de-obstruct them.
19:31/29:39 Infections are very unusual, maybe a mild Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) can occur 6% to 7% of the time.
19:41/29:39 Permanent stress incontinence is very unusual and it occurs about 1% of the time. Stricture rates for the urethra is also around 1% I think. By dilating the urethra and aggressively using lubricant I think that keeps the rate low.
20:28/29:39 One benefit of the laser is you don't have the heat energy like with TURP seeping down the length of the scope.
22:07 anaesthetic with reduced narcotics so the patient has the best option to urinate after surgery; so they are getting very minimal narcotics minimal anaesthetic.
22:15 It is a general anaesthetic as it is a short op. Usually they are out of the hospital within a few hours of surgery.
23:51 but I'm going to look for the ureteral(?) orifice too right there
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Bk_uWuvBzc
NOTE:
Valsalva maneuver can help empty the bladder by straining the abdominal muscles to increase pressure within the bladder. The Valsalva maneuver can be used by those with incomplete spinal cord injuries, as it requires you to bear down and squeeze the abdominal muscles.
https://mtgcatheters.com/adding-voiding-maneuvers-to-your-bladder-management-routine-to-improve-bladder-emptying/
HoLEP Recovery/Risks
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6877364/
HoLEP postoperative complications
1) urethral stricture
2) incontinence (Transient Urinary Incontinence TUI)
3) erectile dysfunction (ED)
4) retrograde ejaculation 92.5% (TURP 70%)
5) bladder neck contraction
TUI, defined as any type of urine leakage, occurred after HoLEP in some patients (16.6%). However, most of these recovered within three months.
*** Recent studies have shown that HoLEP is extremely effective at treating urinary retention.
https://prostatematters.co.uk/benign-prostatic-hyperplasia-bph/treatment-of-bph-turp/
Walking is encouraged from day 1 after HoLEP.
*** HoLEP allows laboratory analysis of the removed prostate tissue like a biopsy
The risks of HoLEP laser treatment of the prostate include:
1) Short term urinary incontinence which resolves within 1 month in 5%
2) Severe urinary incontinence requiring another surgical procedure to correct in 0.5%
3) Backwards ejaculation in more than 90%, although an ejaculation-sparing HoLEP can be offered by experienced HoLEP surgeons and this reduces the risk of backwards ejaculation to around 20%.
4) Weakening of the erections in 2%. It is important to note that erections might improve in 4% of men after HoLEP.
5) Scarring of the urethra (urethral stricture) requiring another procedure to correct in 4%
6) Severe infection requiring readmission to hospital in <0.5%
it is quite common to see some blood in the urine, often intermittently, for even up to 6 weeks after surgery. This is not a concern surgically, and although blood in the urine may seem alarming to some people it is usually only a small amount of blood that is lost. It is very unusual to require a blood transfusion after laser surgery.
https://www.newcastle-hospitals.nhs.uk/services/urology/our-services/laser-prostate-surgery/holep-laser-enucleation-of-prostate/
https://doclibrary-rcht.cornwall.nhs.uk/DocumentsLibrary/RoyalCornwallHospitalsTrust/Forms/ConsentForms/ProcedureSpecificConsentForms/Urology/CHA4298HoLEP.pdf
Downsides of HoLEP leading to:
https://www.baus.org.uk/patients/information_leaflets/177/holmium_laser_enucleation_of_prostate_holep
and
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tuUAhtXBZLk
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4550601/
Risk factors Transient Urinary Incontinence (TUI)
Most ok after 3 mnths
suggest that these factors are associated with urethral sphincter damage because of its compression, stretching, and tearing by the resectoscope during the operation.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29538164/ May 2018
Evidence-based outcomes of holmium laser enucleation of the prostate.
Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) has been a mainstay therapy for the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) for nearly 20 years.
Retrograde ejaculation and Transient urinary incontinence are two problem areas.
Pelvic Floor Exercises
Some HoLEP surgeons never mention pelvic floor exercises to patients
https://www.cambridgeurologypartnership.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/Pelvic-floor-exercises-men-infosheet.pdf
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6979339/
Preoperative pelvic floor muscle exercise for early continence after holmium laser enucleation of the prostate: a randomized controlled study 23 Jan 2020
Conclusions: 'appears to facilitate improvement'